As we transition to an increasingly digital world, cyber threats like phishing scams are unfortunately becoming more common. Dental offices rely heavily on email and so there is a big risk of having credentials stolen, downloading a virus, or even becoming a victim of a devastating ransomware attack.
Particularly prevalent among these threats are scams associated with Microsoft 365, a popular and widely used productivity suite. Let’s explore the common types of Microsoft 365 phishing scams and provide advice on how to protect yourself and your organization.
Common Microsoft 365 Phishing Scams
Phishing scams target unsuspecting users by impersonating trustworthy organizations or individuals, with the aim of tricking users into divulging sensitive information or credentials. Here are some of the common Microsoft 365 phishing scams to watch out for:
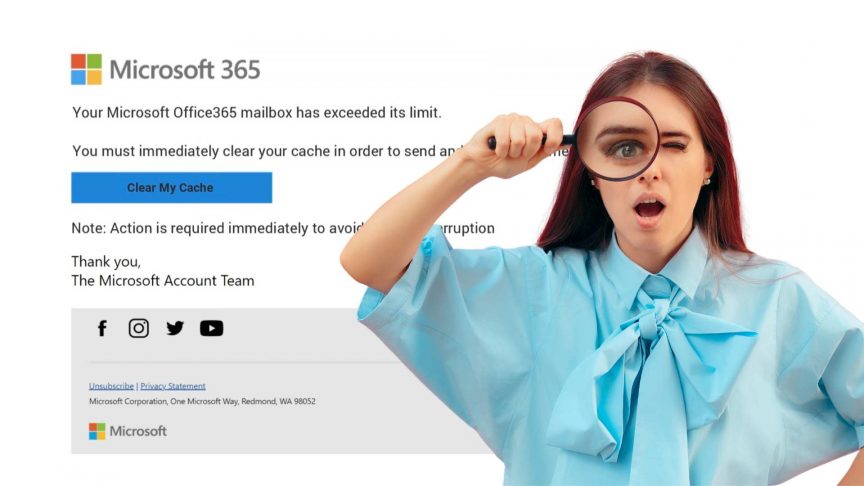
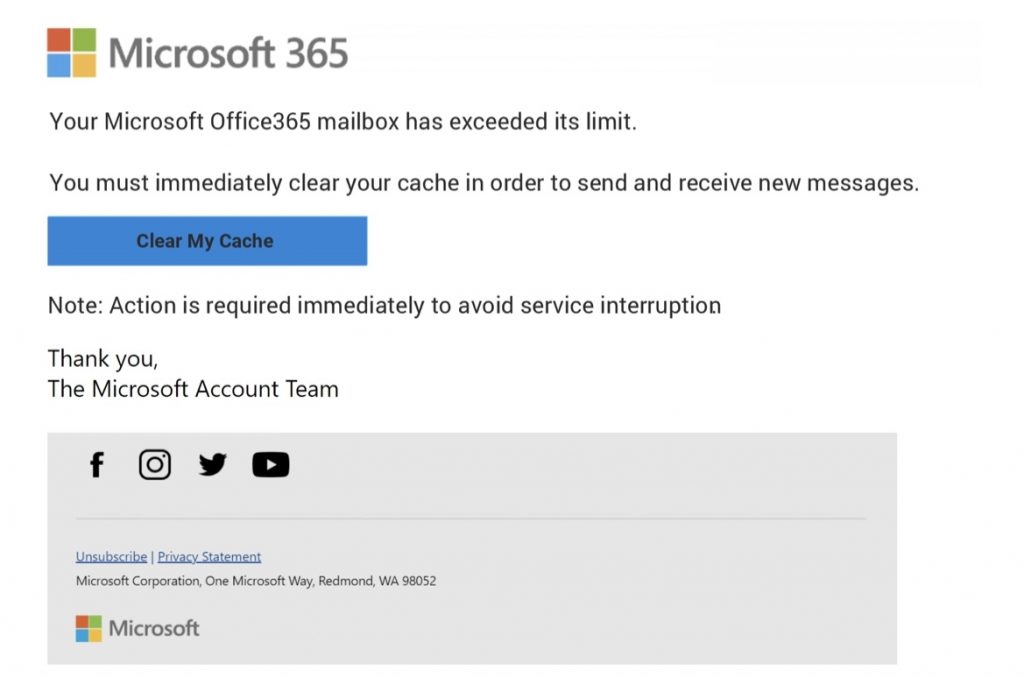
- Email Impersonation Scams: One of the most common phishing tactics is an email claiming to be from Microsoft Support. It may request users to update their login details, often under the guise of a security update or a threat to your account.
- Fake Login Pages: Another common phishing method involves redirecting users to fake Microsoft 365 login pages. The intention here is to harvest your login credentials when you unknowingly input them on the fraudulent page.
- Payment Failure Scams: These scams take the form of an email notifying you that your Microsoft 365 subscription payment has failed. The email will typically ask you to update your payment information through a provided link, leading to a fake page designed to steal your details.
- Document Sharing Scams: Attackers often exploit the collaborative features of Microsoft 365, such as SharePoint or OneDrive, to share malicious links or files that appear to be from trusted contacts or colleagues.
How to Protect Yourself
Defending against these scams requires a multi-pronged approach that combines vigilant user behavior with robust security tools and practices.
- Educate Yourself and Your Team: Understand how phishing works and learn to recognize common signs of phishing emails, such as poor grammar, urgent language, generic greetings, and mismatched email addresses or URLs. Great training for dental teams is available at www.myla.training
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional proof of identity beyond a simple username and password. Even if attackers get hold of your login credentials, they would still need the second form of authentication to access your account.
- Regularly Update and Patch: Ensure that your software, including your operating system, browsers, and email clients, are up-to-date. Many attacks exploit known vulnerabilities in software, which are usually addressed in the latest updates and patches.
- Check Email Sender Details: Carefully check the sender’s email address. Even if the email appears to come from Microsoft, a closer look might reveal it is from a different domain.
- Use Secure and Unique Passwords: Avoid using the same password across multiple platforms. If one account is compromised, others could follow. Consider using a password manager to create and store complex passwords.
- Install a Reliable Security Suite: Use comprehensive security software that includes features such as real-time scanning, automatic updates, and email protection. Alexio Defender is a full cybersecurity suite for dental practices that automates cybersecurity and provides over 50 safeguards.
- Avoid Clicking on Suspicious Links or Attachments: If you receive an unexpected email with a link or an attachment, avoid clicking on it. Instead, contact the supposed sender directly through another communication channel to confirm if they indeed sent it.
Remember, it is always better to be safe than sorry. With the growing reliance on digital platforms like Microsoft 365, it’s crucial to be vigilant and proactive in securing our online spaces. Stay informed, take preventative measures, and continue to foster a culture of cybersecurity within your organization.